In regions when the coastline and the tidal range is low, a sandbar that limits the sea-estuary water exchange is formed in many cases.
Previous findings at the Alexander estuary have shown high level of anoxia, mostly in the deep saltier water. In this study, The Israeli center for estuarine research tested how changes in the sandbar structure and rate of water exchange effect the oxygen concentration in the estuary. For that end, we used an array of logging salinity, temperature and oxygen sensors. Sandbar breaches during stormwater or wave events enables entry of newer seawater to the estuary. The oxygen reach seawater form new body of bottom water at the estuary and replanish the oxygen concentration. The bigger the volume of seawater that enters the estuary, the larger the effect on oxygen concentration and the geographic extent of the effect. Within this research, an analysis of sandbar breaches during the years 2014 to 2018 was conducted. The findings indicate that after rebuilding of the sandbar, oxygen concentration in the bottom water begin to decline due to biogenic uptake. By calculating the effect of the extent of dilution of the bottom water on oxygen concentration (using the change in salinity and oxygen concentration) we found that daily dilution of ~10% seawater will remove the anoxic stress (figure 1).
The assess that such extent of dilution will be hard to achieve and therefore not practical.
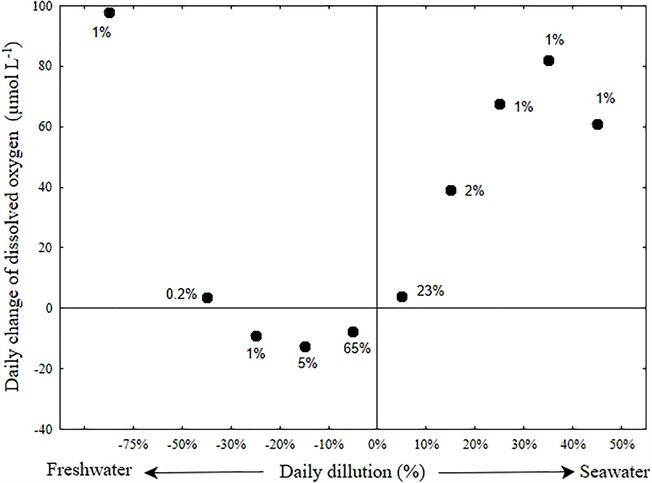
figure 1: dilution diagram of the Alexander estuary bottom water during 559 days of research: The X axis shows the daily dilution with seawater or freshwater and the Y axis indicates the daily oxygen uptake (the percentage of the groups from the total number of research days is indicated for each group).
The term dilution on the X axis indicates the percent of new water that enters the bottom water (salinity decrease for freshwater and increase for saltwater). The term daily oxygen concentration change indicates the difference in the median oxygen concentration between two consecutive days, negative values indicate reduction in oxygen concentration and positive values indicate an increased oxygen concentration.


